Figure 1
Download original image
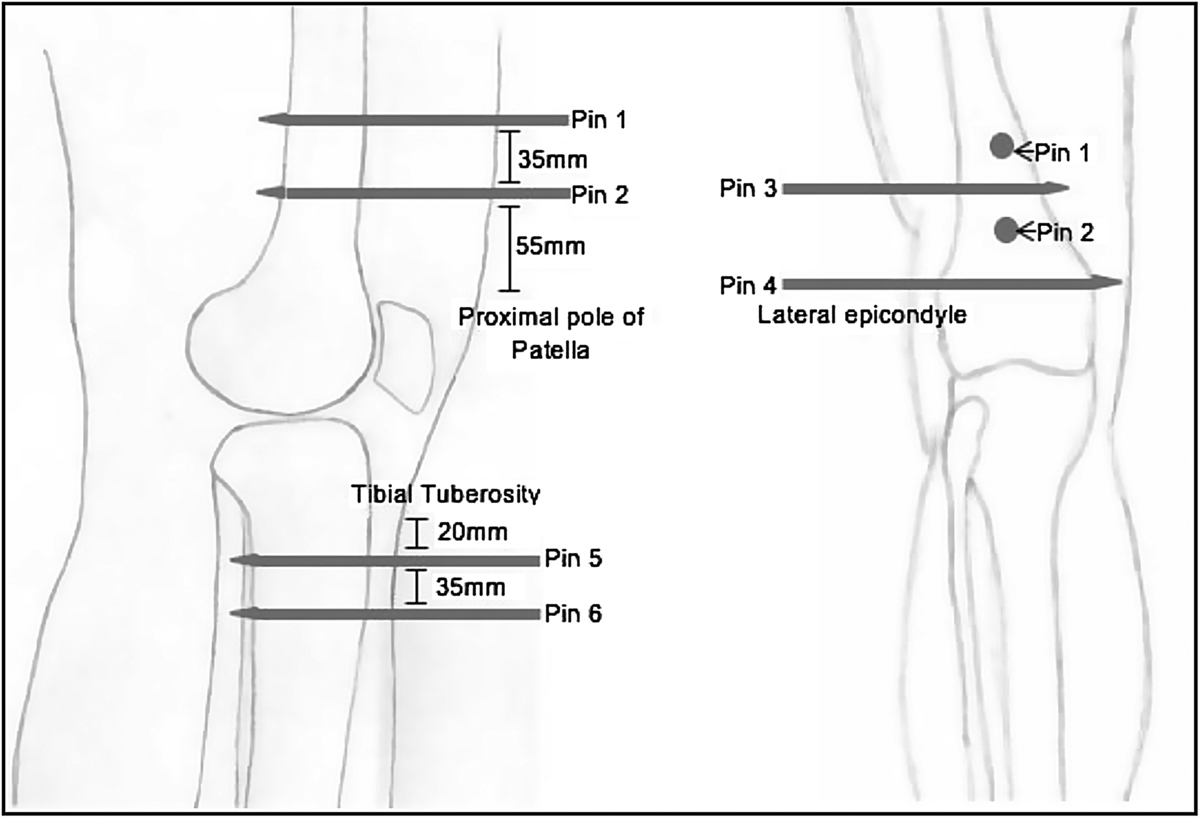
This figure illustrates the positions of the six EF pins and shows how the tips of the EF pins pass through to the other side of the bone, endangering the neurovasculature. The pins were placed specifically about the knee, within the metaphyseal/metadiaphyseal portions of the tibia/femur relative to the knee joint. The focus was on proximity that the EF pin tips obtained to the neurovascular bundle within these areas, as opposed to the stabilization constructs.
The pins were inserted in orthogonal planes and perpendicular to the axes of the limb, the exact locations are described below:
-
Pin 1 – inserted anterior to posterior within the distal femur, 90 mm ± proximal to the proximal pole of the patella.
-
Pin 2 – inserted anterior to posterior within the distal femur, 55 mm ± proximal to the proximal pole of the patella.
-
Pin 3 – inserted lateral to medial in the distal femur, approximately 100 mm ± proximal to the lateral epicondyle.
-
Pin 4 – inserted lateral to medial in the distal femur, positioned 30 mm ± proximal to the lateral epicondyle.
-
Pin 5 – inserted anterior to posterior in the proximal tibia; 20 mm ± below the tuberosity and 2 mm ± medially. This placed the pin parallel to the lateral wall of the tibia, once it had been drilled into place.
-
Pin 6 – inserted anterior to posterior in the proximal tibia; 35 mm ± distally to pin 5.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


