Figure 2
Download original image
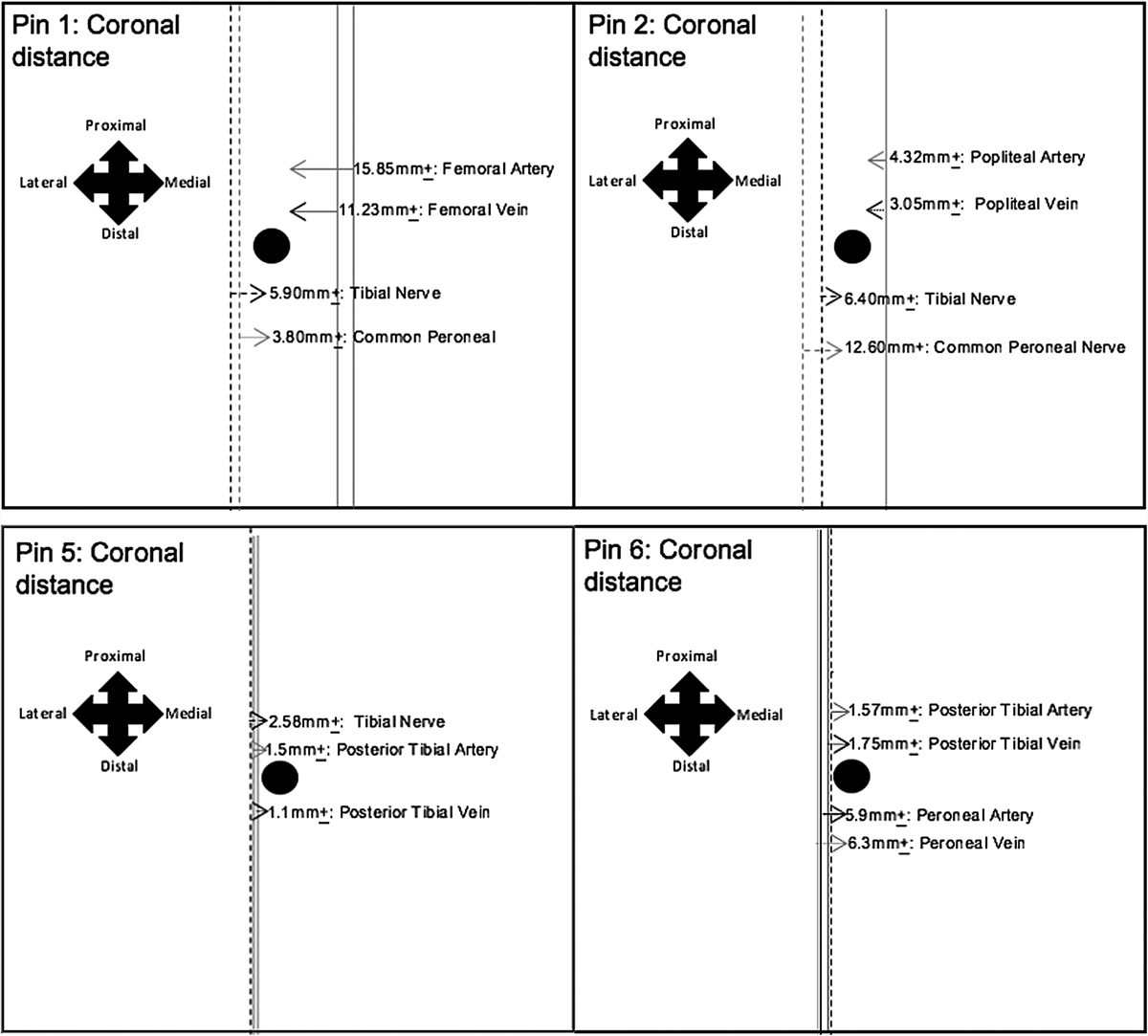
The results show that the tips of EF pins 1 and 2 attained a close proximity to the large neurovasculature, within the coronal plane, specifically; the tibial and common peroneal nerve and the femoral/popliteal vessels, respectively. Moreover, the measurements obtained for the average coronal distances, between the tibial nerve and pin 2, differed within the left and right distal thighs; highlighting neurovascular variation. Additionally, the tips of pins 5 and 6 also attained a close proximity to the large neurovasculature; as shown in the figure. Therefore, it would be beneficial to modify the locations of EF pins 1, 2, 5 and 6, in order to reduce the risk of iatrogenic injury to these vessels.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


